
- Bioactive Compounds
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at [email protected] to customize your library.
You could select:
- Antibodies
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-DYKDDDDK Tag magnetic beads
- Anti-DYKDDDDK Tag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Poly DYKDDDDK Tag Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- New Products
- Contact Us
Dovitinib (TKI-258)
Synonyms: CHIR-258
Dovitinib (TKI258, CHIR258) is a multitargeted RTK inhibitor, mostly for class III (FLT3/c-Kit) with IC50 of 1 nM/2 nM, also potent to class IV (FGFR1/3) and class V (VEGFR1-4) RTKs with IC50 of 8-13 nM, less potent to InsR, EGFR, c-Met, EphA2, Tie2, IGF-1R and HER2 in cell-free assays. Phase 4.
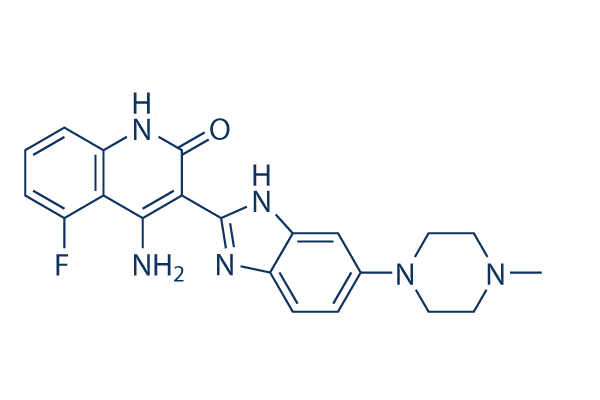
Dovitinib (TKI-258) Chemical Structure
CAS: 405169-16-6
Selleck's Dovitinib (TKI-258) has been cited by 50 publications
Purity & Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.98%
99.98
Other FLT3 Products
Related compound libraries
Choose Selective FLT3 Inhibitors
Cell Data
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SupB15 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.449 μM | 25202073 | |||
| SupB15-R | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.558 μM | 25202073 | |||
| BaF3-pSRα | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.668 μM | 25202073 | |||
| BaF3-p210Bcr-Abl | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.692 μM | 25202073 | |||
| BaF3-p210Bcr-Abl-T315I | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.626 μM | 25202073 | |||
| CCRF-CEM | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.398 μM | 25202072 | |||
| CEM/C2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.125 μM | 25202072 | |||
| Nalm-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.382 μM | 25202072 | |||
| SEM-K2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.022 μM | 25202072 | |||
| HB-1119 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.028 μM | 25202072 | |||
| RS4:11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.81 μM | 25202072 | |||
| Nalm-6 | Apoptosis Assay | 2 μM | 24/48 h | induces apoptosis resulting in about 72% of cell death after 24 h treatment and 81% after 48 h | 25202072 | |
| SEM-K2 | Apoptosis Assay | 0.1/1 μM | 24 h | induces early apoptosis of SEM-K2 cells at 0.1 μM after 24 h | 25202072 | |
| HCT-116 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.050.58 μM | 24495750 | |||
| HT-29 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.21.93 μM | 24495750 | |||
| SW-480 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.330.47 μM | 24495750 | |||
| CaCO2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.230.64 μM | 24495750 | |||
| LS174T | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.330.47 μM | 24495750 | |||
| HEC-1A | Function Assay | 0.05/0.1/0.5 μM | 72 h | causes a decrease in STAT3, ERK, and AKT phosphorylation | 24495750 | |
| AN3CA | Function Assay | 0.05/0.1/0.5 μM | 72 h | causes a decrease in STAT3, ERK, and AKT phosphorylation | 24495750 | |
| MFE-296 | Function Assay | 0.05/0.1/0.5 μM | 72 h | causes a decrease in STAT3, ERK, and AKT phosphorylation | 24495750 | |
| UMC3 | Cell Viability Assay | 1-10 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 24325461 | |
| 5637 | Cell Viability Assay | 1-10 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 24325461 | |
| HU456 | Cell Viability Assay | 1-10 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 24325461 | |
| MGHU4 | Cell Viability Assay | 1-10 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 24325461 | |
| HT1376 | Cell Viability Assay | 1-10 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 24325461 | |
| RT112 | Cell Viability Assay | 1-10 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 24325461 | |
| T24 | Cell Viability Assay | 1-10 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 24325461 | |
| BFTC905 | Cell Viability Assay | 1-10 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 24325461 | |
| TCC-SUP | Cell Viability Assay | 1-10 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 24325461 | |
| RT4 | Cell Viability Assay | 1-10 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 24325461 | |
| HONE1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.1-10 μM | 48 h | induces G2/M delay in a concentration-dependent manner | 24238094 | |
| HNE1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.1-10 μM | 48 h | induces G2/M delay in a concentration-dependent manner | 24238094 | |
| CNE2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.1-10 μM | 48 h | induces G2/M delay in a concentration-dependent manner | 24238094 | |
| C666-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.1-10 μM | 48 h | induces G2/M delay in a concentration-dependent manner | 24238094 | |
| HeLa | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.1-10 μM | 24 h | induces G2/M arrest in a concentration-dependent manner | 24238094 | |
| Hep3B | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.1-10 μM | 24 h | induces G2 arrest | 24238094 | |
| HepG2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | IC50=2.727 ± 0.429 μM | 23546591 | ||
| Hep3B | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | IC50=4.223 ± 0.839 μM | 23546591 | ||
| PLC/PRF5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | IC50=16.120 ± 4.001 μM | 23546591 | ||
| Huh7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | IC50=15.007 ± 7.334 μM | 23546591 | ||
| HepG2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=1.200 ± 0.226 μM | 23546591 | ||
| Hep3B | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=0.892 ± 0.044 μM | 23546591 | ||
| PLC/PRF5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=3.110 ± 0.337 μM | 23546591 | ||
| Huh7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=3.980 ± 0.803 μM | 23546591 | ||
| MFE280 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.42 ± 0.06 μM | 23443805 | |||
| AN3CA | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.50 ± 0.10 μM | 23443805 | |||
| HEC155 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.66 ± 0.09 μM | 23443805 | |||
| MFE296 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.66 ± 0.19 μM | 23443805 | |||
| SPAC1S | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.77 ± 0.08 μM | 23443805 | |||
| RL952 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.93 ± 0.01 μM | 23443805 | |||
| EN1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.02 ± 0.25 μM | 23443805 | |||
| SNGII | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.24 ± 0.28 μM | 23443805 | |||
| ISHIKAWA | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.30 ± 0.11 μM | 23443805 | |||
| HEC1A | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.34 ± 0.30 μM | 23443805 | |||
| KLE | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.37 ± 0.02 μM | 23443805 | |||
| SNGM | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.42 ± 0.13 μM | 23443805 | |||
| USPC2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.62 ± 0.01 μM | 23443805 | |||
| EN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.66 ± 0.01 μM | 23443805 | |||
| MFE319 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.87 ± 0.45 μM | 23443805 | |||
| EFE184 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.04 ± 0.13 μM | 23443805 | |||
| ECC1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.07 ± 0.01 μM | 23443805 | |||
| HEC1B | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.57 ± 0.23 μM | 23443805 | |||
| USPC1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.60 ± 0.13 μM | 23443805 | |||
| SPAC1L | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.06 ± 1.14 μM | 23443805 | |||
| HUVEC | Cell Viability Assay | 0-25 μM | 72 h | DMSO | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 23228017 |
| HMVEC | Cell Viability Assay | 0-25 μM | 72 h | DMSO | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 23228017 |
| MHCC-97H | Cell Viability Assay | 0-25 μM | 72 h | DMSO | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 23228017 |
| SMMC7721 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-25 μM | 72 h | DMSO | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 23228017 |
| Huh-7 | Apoptosis Assay | 0-12.5 μM | 24 h | DMSO | sensitizes HCC cells to TRAIL- and tigatuzumab-induced apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner | 22230479 |
| Sk-Hep1 | Apoptosis Assay | 0-12.5 μM | 24 h | DMSO | sensitizes HCC cells to TRAIL- and tigatuzumab-induced apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner | 22230479 |
| Hep3B | Apoptosis Assay | 0-12.5 μM | 24 h | DMSO | sensitizes HCC cells to TRAIL- and tigatuzumab-induced apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner | 22230479 |
| PLC5 | Apoptosis Assay | 0-12.5 μM | 24 h | DMSO | sensitizes HCC cells to TRAIL- and tigatuzumab-induced apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner | 22230479 |
| PLC5 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-15 μM | 72 h | reduces cell viability in a dose-dependent manner | 22180308 | |
| Hep3B | Cell Viability Assay | 0-15 μM | 72 h | reduces cell viability in a dose-dependent manner | 22180308 | |
| Sk-Hep1 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-15 μM | 72 h | reduces cell viability in a dose-dependent manner | 22180308 | |
| Huh-7 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-15 μM | 72 h | reduces cell viability in a dose-dependent manner | 22180308 | |
| PLC5 | Apoptosis Assay | 0-15 μM | 24 h | increases apoptotic cell death in a dose-dependent manner | 22180308 | |
| Hep3B | Apoptosis Assay | 0-15 μM | 24 h | increases apoptotic cell death in a dose-dependent manner | 22180308 | |
| Sk-Hep1 | Apoptosis Assay | 0-15 μM | 24 h | increases apoptotic cell death in a dose-dependent manner | 22180308 | |
| Huh-7 | Apoptosis Assay | 0-15 μM | 24 h | increases apoptotic cell death in a dose-dependent manner | 22180308 | |
| PLC5 | Function Assay | 0-10 μM | 24 h | causes dose-dependent DNA fragmentation | 22180308 | |
| Hep3B | Function Assay | 0-10 μM | 24 h | causes dose-dependent DNA fragmentation | 22180308 | |
| Sk-Hep1 | Function Assay | 0-10 μM | 24 h | causes dose-dependent DNA fragmentation | 22180308 | |
| Huh-7 | Function Assay | 0-10 μM | 24 h | causes dose-dependent DNA fragmentation | 22180308 | |
| SW780 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 5 d | IC50=50 nM | 21119661 | ||
| RT112 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 5 d | IC50=15 nM | 21119661 | ||
| RT4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 5 d | IC50=5 nM | 21119661 | ||
| JMSU1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 5 d | IC50=50 nM | 21119661 | ||
| J82 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 5 d | IC50=1400 nM | 21119661 | ||
| 97-7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 5 d | IC50=1000 nM | 21119661 | ||
| RT112 | Function Assay | 500 nM | 24 h | increases the proportion of cells in G1 accompanied by a decrease in S and G2/M phases | 21119661 | |
| RT4 | Function Assay | 500 nM | 24 h | increases the proportion of cells in G1 accompanied by a decrease in S and G2/M phases | 21119661 | |
| MGH-U3 | Function Assay | 500 nM | 24 h | increases the proportion of cells in G1 accompanied by a decrease in S and G2/M phases | 21119661 | |
| SW780 | Function Assay | 500 nM | 24 h | increases the proportion of cells in G1 accompanied by a decrease in S and G2/M phases | 21119661 | |
| 97-7 | Function Assay | 500 nM | 24 h | increases the proportion of cells in G1 accompanied by a decrease in S and G2/M phases | 21119661 | |
| J807C | Cell Viability Assay | 0-400 nM | 48 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 15598814 | |
| Y373C | Cell Viability Assay | 0-400 nM | 48 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 15598814 | |
| K650E | Cell Viability Assay | 0-400 nM | 48 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 15598814 | |
| G384D | Cell Viability Assay | 0-400 nM | 48 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 15598814 | |
| F384L | Cell Viability Assay | 0-400 nM | 48 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 15598814 | |
| KMS11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=90 nM | 15598814 | ||
| KMS18 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=550 nM | 15598814 | ||
| OPM2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=90 nM | 15598814 | ||
| H929 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50> 2500 nM | 15598814 | ||
| 8226 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50> 2500 nM | 15598814 | ||
| U266 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50> 2500 nM | 15598814 | ||
| KM12L4A | Function assay | Inhibition of VEGFR2 phosphorylation expressed in human KM12L4A cells by Western blot analysis, EC50=0.046μM | 19113866 | |||
| KM12L4A | Function assay | Inhibition of PDGFRbeta phosphorylation expressed in human KM12L4A cells Western blot analysis, EC50=0.051μM | 19113866 | |||
| KM12L4A | Function assay | Inhibition of FGFR1 phosphorylation expressed in human KM12L4A cells by Western blot analysis, EC50=0.166μM | 19113866 | |||
| insect cells | Function assay | 1 to 4 hrs | Inhibition of recombinant PDGFRbeta (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected insect cells using biotinylated peptide substrate GGLFDDPSYVNVQNL in presence of ATP incubated for 1 to 4 hrs by time resolved fluorescence assay, IC50=0.001μM | 27914362 | ||
| Sf9 | Function assay | 1 to 4 hrs | Inhibition of recombinant human N-terminal GST/His6-tagged c-KIT (544 to 976 residues) expressed in baculovirus infected sf9 cells using biotinylated peptide substrate GGLFDDPSYVNVQNL in presence of ATP incubated for 1 to 4 hrs by time resolved fluorescen, IC50=0.001μM | 27914362 | ||
| Sf9 | Function assay | 1 to 4 hrs | Inhibition of recombinant human N-terminal GST/His6-tagged FLT3 (571 to 993 residues) expressed in baculovirus infected sf9 cells using biotinylated peptide substrate GGLFDDPSYVNVQNL in presence of ATP incubated for 1 to 4 hrs by time resolved fluorescenc, IC50=0.001μM | 27914362 | ||
| insect cells | Function assay | 1 to 4 hrs | Inhibition of recombinant FGFR1 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected insect cells using biotinylated peptide substrate GGGGQDGKDYIVLPI in presence of ATP incubated for 1 to 4 hrs by time resolved fluorescence assay, IC50=0.008μM | 27914362 | ||
| insect cells | Function assay | 1 to 4 hrs | Inhibition of recombinant VEGFR3 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected insect cells using biotinylated peptide substrate GGGGQDGKDYIVLPI in presence of ATP incubated for 1 to 4 hrs by time resolved fluorescence assay, IC50=0.008μM | 27914362 | ||
| insect cells | Function assay | 1 to 4 hrs | Inhibition of recombinant VEGFR1 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected insect cells using biotinylated peptide substrate GGGGQDGKDYIVLPI in presence of ATP incubated for 1 to 4 hrs by time resolved fluorescence assay, IC50=0.01μM | 27914362 | ||
| insect cells | Function assay | 1 to 4 hrs | Inhibition of recombinant VEGFR2 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected insect cells using biotinylated peptide substrate GGGGQDGKDYIVLPI in presence of ATP incubated for 1 to 4 hrs by time resolved fluorescence assay, IC50=0.013μM | 27914362 | ||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| insect cells | Function assay | 1 to 4 hrs | Inhibition of recombinant FGFR1 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected insect cells using GGGGQDGKDYIVLPI as substrate after 1 to 4 hrs by time-resolved fluorescence assay, IC50=0.008μM | 30503938 | ||
| NCI-H1703 | Function assay | 10 uM | 24 hrs | Inhibition of TNIK in human NCI-H1703 cells transfected with lentiviral vector 7TFP assessed as reduction of GSK3 inhibitor X activated TNIK-mediated Wnt/TCF/beta-catenin-dependent transcription at 10 uM after 24 hrs by luciferase reporter assay | ChEMBL | |
| LoVo | Cytotoxicity assay | 10 uM | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against Wnt/beta-catenin signalling dependent human LoVo cells assessed as cell viability at 10 uM after 72 hrs by ATPlite assay | ChEMBL | |
| HCT116 | Cytotoxicity assay | 10 uM | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against Wnt/beta-catenin signalling dependent human HCT116 cells assessed as cell viability at 10 uM after 72 hrs by ATPlite assay | ChEMBL | |
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Biological Activity
| Description | Dovitinib (TKI258, CHIR258) is a multitargeted RTK inhibitor, mostly for class III (FLT3/c-Kit) with IC50 of 1 nM/2 nM, also potent to class IV (FGFR1/3) and class V (VEGFR1-4) RTKs with IC50 of 8-13 nM, less potent to InsR, EGFR, c-Met, EphA2, Tie2, IGF-1R and HER2 in cell-free assays. Phase 4. | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
| In vitro | ||||
| In vitro | Dovitinib potently inhibits the FGF-stimulated growth of WT and F384L-FGFR3-expressing B9 cells with IC50 of 25 nM. In addition, Dovitinib inhibits proliferation of B9 cells expressing each of the various activated mutants of FGFR3. Interestingly, there are minimal observed differences in the sensitivity of the different FGFR3 mutations to Dovitinib, with the IC50 ranging from 70 to 90 nM for each of the various mutations. IL-6-dependent B9 cells containing vector only (B9-MINV cells are resistant to the inhibitory activity of Dovitinib at concentrations up to 1 μM. Dovitinib inhibits cell proliferation of KMS11 (FGFR3-Y373C), OPM2 (FGFR3-K650E), and KMS18 (FGFR3-G384D) cells with IC50 of 90 nM (KMS11 and OPM2) and 550 nM, respectively. Dovitinib inhibits FGF-mediated ERK1/2 phosphorylation and induces cytotoxicity in FGFR3-expressing primary MM cells. BMSCs does confer a modest degree of resistance with 44.6% growth inhibition for cells treated with 500 nM Dovitinib and cultured on stroma compared with 71.6% growth inhibition for cells grown without BMSCs. Dovitinib inhibits proliferation of M-NFS-60, an M-CSF growth-driven mouse myeloblastic cell line with a median effective concentration (EC50) of 220 nM. [1] Treatment of SK-HEP1 cells with Dovitinib results in a dose-dependent reduction in cell number and G2/M phase arrest with reduction in the G0/G1 and S phases, inhibition of anchorage-independent growth and blockage of bFGF-induced cell motility. The IC50 for Dovitinib in SK-HEP1 cells is approximately 1.7 μM. Dovitinib also significantly reduces the basal phosphorylation levels of FGFR-1, FGFR substrate 2α (FRS2-α) and ERK1/2 but not Akt in both SK-HEP1 and 21-0208 cells. In 21-0208 HCC cells, Dovitinib significantly inhibits bFGF-induced phosphorylation of FGFR-1, FRS2-α, ERK1/2 but not Akt. [2] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinase Assay | In vitro kinase assays | |||
| The inhibitory concentration of 50% (IC50) values for the inhibition of RTKs by Dovitinib are determined in a time-resolved fluorescence (TRF) or radioactive format, measuring the inhibition by Dovitinib of phosphate transfer to a substrate by the respective enzyme. The kinase domains of FGFR3, FGFR1, PDGFRβ, and VEGFR1-3 are assayed in 50 mM HEPES (N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N′-2-ethanesulfonic acid), pH 7.0, 2 mM MgCl2, 10 mM MnCl2 1 mM NaF, 1 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), 1 mg/mL bovine serum albumin (BSA), 0.25 μM biotinylated peptide substrate (GGGGQDGKDYIVLPI), and 1 to 30 μM adenosine triphosphate (ATP) depending on the Km for the respective enzyme. ATP concentrations are at or just below Km. For c-KIT and FLT3 reactions the pH is raised to 7.5 with 0.2 to 8 μM ATP in the presence of 0.25 to 1 μM biotinylated peptide substrate (GGLFDDPSYVNVQNL). Reactions are incubated at room temperature for 1 to 4 hours and the phosphorylated peptide captured on streptavidin-coated microtiter plates containing stop reaction buffer (25 mM EDTA [ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid], 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5). Phosphorylated peptide is measured with the DELFIA TRF system using a Europium-labeled antiphosphotyrosine antibody PT66. The concentration of Dovitinib for IC50 is calculated using nonlinear regression with XL-Fit data analysis software version 4.1 (IDBS). Inhibition of colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF-1R), PDGFRα, insulin receptor (InsR), and insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGFR1) kinase activity is determined at ATP concentrations close the Km for ATP. | ||||
| Cell Research | Cell lines | B9 cells, MM cell lines | ||
| Concentrations | 100 nM | |||
| Incubation Time | 48-96 hours | |||
| Method | Cell viability is assessed by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium (MTT) dye absorbance. Cells are seeded in 96-well plates at a density of 5 × 103 (B9 cells) or 2 × 104 (MM cell lines) cells per well. Cells are incubated with 30 ng/mL aFGF and 100 μg/mL heparin or 1% IL-6 where indicated and increasing concentrations of Dovitinib. For each concentration of Dovitinib, 10 μL aliquots of drug or DMSO diluted in culture medium is added. For drug combination studies, cells are incubated with 0.5 μM dexamethasone, 100 nM Dovitinib, or both simultaneously where indicated. To evaluate the effect of Dovitinib on growth of MM cells adherent to BMSCs, 104 KMS11 cells are cultured on BMSC-coated 96-well plates in the presence or absence of Dovitinib. Plates are incubated for 48 to 96 hours. For assessment of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF)-mediated growth, 5 × 103 M-NFS-60 cells/well are incubated with serial dilutions of Dovitinib with 10 ng/mL M-CSF and without granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). After 72 hours cell viability is determined using Cell Titer-Glo Assay. Each experimental condition is performed in triplicate. | |||
| Experimental Result Images | Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
| Western blot | CDK1 / p-CDK1 / p53 / p21 p-PDGFR-β / PDGFR-β / p-ERK / ERK p-VEGFR-2 / VEGFR-2 / p-FGFR-1 / FGFR-1 p-STAT3 / STAT3 / Mcl-1 / LC3 / Beclin 1 / p62 |
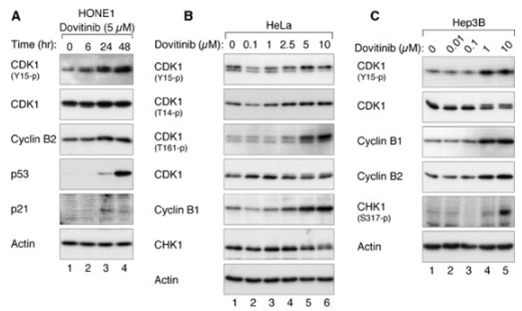
|
24238094 | |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
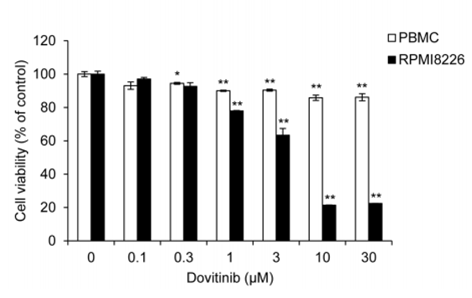
|
28467797 | |
| In Vivo | ||
| In vivo | Dovitinib induces both cytostatic and cytotoxic responses in vivo resulting in regression of FGFR3-expressing tumors.[1] Dovitinib shows a dose- and exposure-dependent inhibition of target receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) expressed in tumor xenografts. Dovitinib potently inhibits tumor growth of six HCC lines. Inhibition of angiogenesis correlated with inactivation of FGFR/PDGFRβ/VEGFR2 signaling pathways. In an orthotopic model, Dovitinib potently inhibits primary tumor growth and lung metastasis and significantly prolonged mouse survival. [2] Administration of Dovitinib results in significant tumor growth inhibition and tumor regressions, including large, established tumors (500-1,000 mm3). [3] | |
|---|---|---|
| Animal Research | Animal Models | 8-week-old female BNX mice bearing KMS11 cells |
| Dosages | 10, 30, or 60 mg/kg | |
| Administration | Gavage | |
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05571969 | Recruiting | Advanced Solid Tumors | Allarity Therapeutics|Amarex Clinical Research | February 20 2023 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02268435 | Withdrawn | Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors | Asan Medical Center | March 2015 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01700270 | Completed | Advanced Solid Tumors Excluding Breast Cancer | Novartis Pharmaceuticals|Novartis | May 2013 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01680796 | Withdrawn | Multiple Myeloma | University of Florida|Novartis Pharmaceuticals | February 2013 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01266070 | Terminated | Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome | M.D. Anderson Cancer Center|Novartis | November 2012 | Phase 2 |
Chemical lnformation & Solubility
| Molecular Weight | 392.43 | Formula | C21H21FN6O |
| CAS No. | 405169-16-6 | SDF | Download Dovitinib (TKI-258) SDF |
| Smiles | CN1CCN(CC1)C2=CC3=C(C=C2)N=C(N3)C4=C(C5=C(C=CC=C5F)NC4=O)N | ||
| Storage (From the date of receipt) | |||
|
In vitro |
DMSO : 30 mg/mL ( (76.44 mM); Moisture-absorbing DMSO reduces solubility. Please use fresh DMSO.) Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molecular Weight Calculator |
|
In vivo Add solvents to the product individually and in order. |
In vivo Formulation Calculator |
||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Molarity Calculator
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Tech Support
Answers to questions you may have can be found in the inhibitor handling instructions. Topics include how to prepare stock solutions, how to store inhibitors, and issues that need special attention for cell-based assays and animal experiments.
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
* Indicates a Required Field
Tags: buy Dovitinib (TKI-258) | Dovitinib (TKI-258) supplier | purchase Dovitinib (TKI-258) | Dovitinib (TKI-258) cost | Dovitinib (TKI-258) manufacturer | order Dovitinib (TKI-258) | Dovitinib (TKI-258) distributor







































