
- Bioactive Compounds
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at [email protected] to customize your library.
You could select:
- Antibodies
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-DYKDDDDK Tag magnetic beads
- Anti-DYKDDDDK Tag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Poly DYKDDDDK Tag Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- New Products
- Contact Us
Aspirin
Synonyms: NSC 27223, Acetylsalicylic acid, ASA
Aspirin is a salicylate, and irreversible COX1 and COX2 inhibitor, used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains, as an antipyretic to reduce fever, and as an anti-inflammatory medication. Aspirin induces autophagy and stimulates mitophagy.
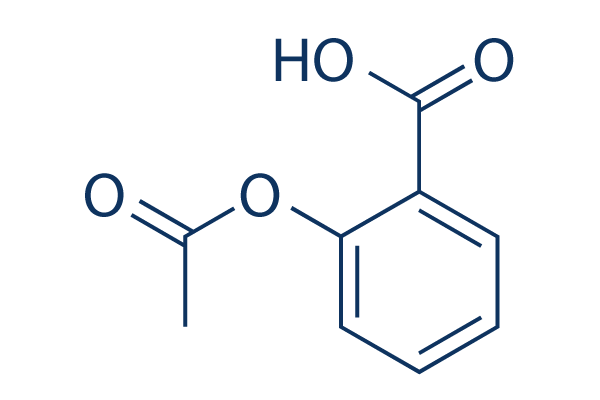
Aspirin Chemical Structure
CAS: 50-78-2
Selleck's Aspirin has been cited by 25 publications
Purity & Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.99%
99.99
Other COX Products
Related compound libraries
Choose Selective COX Inhibitors
Cell Data
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGS | Function assay | 15 to 60 umol/L after | 12 hrs | Inhibition of Escherichia coli-stimulated IL-8 production in human AGS cells at 15 to 60 umol/L after 12 hrs by ELISA | 20153183 | |
| microglia cells | Antineuroinflammatory assay | 15 mins | Antineuroinflammatory activity in LPS-stimulated rat microglia cells assessed as inhibition of PMA-stimulated TXB2 release preincubated for 15 mins measured 70 mins after PMA challenge, IC50=3.12μM | 22153874 | ||
| HCT116 | Function assay | 1 mM | 6 hrs | Inhibition of TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation in human HCT116 cells at 1 mM after 6 hrs by luciferase reporter gene assay | 22154834 | |
| SKBR3 | Growth inhibition assay | 300 uM | 48 hrs | Growth inhibition of human SKBR3 cells at 300 uM after 48 hrs by alamar blue assay | 22494617 | |
| PANC1 | Growth inhibition assay | 300 uM | 48 hrs | Growth inhibition of human PANC1 cells at 300 uM after 48 hrs by alamar blue assay | 22494617 | |
| PC3 | Growth inhibition assay | 300 uM | 48 hrs | Growth inhibition of human PC3 cells at 300 uM after 48 hrs by alamar blue assay | 22494617 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function assay | 100 uM | 30 mins | Irreversible inhibition of COX-1 in human MDA-MB-231 cells assessed as inhibition of arachidonic acid-induced PGE2 formation at 100 uM incubated for 30 mins followed by compound washout measured 30 mins post arachidonic acid challenge by radioimmunoassay | 23651359 | |
| THP1 | Function assay | 100 uM | 30 mins | Irreversible inhibition of COX-1 in human THP1 cells assessed as inhibition of arachidonic acid-induced TXB2 formation at 100 uM incubated for 30 mins followed by compound washout measured 30 mins post arachidonic acid challenge by radioimmunoassay | 23651359 | |
| HCT116 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human HCT116 cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 48 hrs MTT assay | 26750401 | ||
| H9c2 | Cardioprotective assay | 1 uM | 8 hrs | Cardioprotective activity against hypoxia-induced oxidative stress mediated inflammation in rat H9c2 cells assessed as suppression of IL-6 in supernatant at 1 uM preincubated for 8 hrs followed by H2O2 addition for 2 hrs by ELISA | 27575471 | |
| H9c2 | Cardioprotective assay | 1 uM | 8 hrs | Cardioprotective activity against hypoxia-induced oxidative stress mediated inflammation in rat H9c2 cells assessed as suppression of TNF-alpha in supernatant at 1 uM preincubated for 8 hrs followed by H2O2 addition for 2 hrs in presence of leonurine by E | 27575471 | |
| H9c2 | Cardioprotective assay | 1 uM | 8 hrs | Cardioprotective activity against hypoxia-induced oxidative stress in rat H9c2 cells assessed as antioxidant activity by measuring reduction in MDA levels at 1 uM preincubated for 8 hrs followed by H2O2 addition for 2 hrs by spectrophotometry | 27575471 | |
| H9c2 | Cardioprotective assay | 1 uM | 8 hrs | Cardioprotective activity against hypoxia-induced oxidative stress in rat H9c2 cells assessed as antioxidant activity by measuring increase in SOD activity at 1 uM preincubated for 8 hrs followed by H2O2 addition for 2 hrs by spectrophotometry | 27575471 | |
| H9c2 | Cardioprotective assay | 1 uM | 8 hrs | Cardioprotective activity against hypoxia-induced oxidative stress in rat H9c2 cells assessed as antioxidant activity by measuring increase in catalase activity at 1 uM preincubated for 8 hrs followed by H2O2 addition for 2 hrs by spectrophotometry | 27575471 | |
| H9c2 | Cardioprotective assay | 1 uM | 8 hrs | Cardioprotective activity against hypoxia-induced oxidative stress mediated inflammation in rat H9c2 cells assessed as suppression of TNF-alpha in supernatant at 1 uM preincubated for 8 hrs followed by H2O2 addition for 2 hrs by ELISA | 27575471 | |
| H9c2 | Cardioprotective assay | 1 uM | 8 hrs | Cardioprotective activity against hypoxia-induced oxidative stress mediated inflammation in rat H9c2 cells assessed as suppression of IL-1beta in supernatant at 1 uM preincubated for 8 hrs followed by H2O2 addition for 2 hrs by ELISA | 27575471 | |
| H9c2 | Cardioprotective assay | 1 uM | 8 hrs | Cardioprotective activity against hypoxia-induced oxidative stress in rat H9c2 cells assessed as reduction in MDA levels at 1 uM preincubated for 8 hrs followed by H2O2 addition for 2 hrs in presence of leonurine by spectrophotometry | 27575471 | |
| H9c2 | Cardioprotective assay | 1 uM | 8 hrs | Cardioprotective activity against hypoxia-induced oxidative stress in rat H9c2 cells assessed as antioxidant activity by measuring increase in SOD activity at 1 uM preincubated for 8 hrs followed by H2O2 addition for 2 hrs in presence of leonurine by spec | 27575471 | |
| H9c2 | Cardioprotective assay | 1 uM | 8 hrs | Cardioprotective activity against hypoxia-induced oxidative stress mediated inflammation in rat H9c2 cells assessed as suppression of IL-6 in supernatant at 1 uM preincubated for 8 hrs followed by H2O2 addition for 2 hrs in presence of leonurine by ELISA | 27575471 | |
| H9c2 | Cardioprotective assay | 1 uM | 8 hrs | Cardioprotective activity against hypoxia-induced oxidative stress mediated inflammation in rat H9c2 cells assessed as suppression of IL-1beta in supernatant at 1 uM preincubated for 8 hrs followed by H2O2 addition for 2 hrs in presence of leonurine by EL | 27575471 | |
| H9c2 | Cardioprotective assay | 1 uM | 8 hrs | Cardioprotective activity against hypoxia-induced cytotoxicity in rat H9c2 cells assessed as increase in cell viability at 1 uM preincubated for 8 hrs followed by H2O2 addition for 2 hrs by MTT assay | 27575471 | |
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | Antiinflammatory activity in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of LPS-induced nitric oxide production by measuring nitrite accumulation by Griess method, IC50=43.2μM | 28561586 | |||
| stem cells | Function assay | 100 uM | 5 days | Induction of adipogenesis in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells assessed as increase in adiponectin production at 100 uM measured on day 5 in presence of IDX by ELISA | 29398443 | |
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| peritoneal cells | Function assay | 5 hrs | Inhibition of LPS-induced PGE2 production in C57BL6 mouse peritoneal cells measured at 5 hrs time interval by ELISA, IC50=4.08μM | 30006172 | ||
| HCT8 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human HCT8 cells after 72 hrs in presence of cinnamaldehyde by MTT assay, IC50=15.6μM | 30037494 | ||
| RPMI8226 | Cell cycle assay | 1.7 uM | 48 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human RPMI8226 cells assessed as accumulation at G0/G1 phase at 1.7 uM in presence of bortezomib after 48 hrs by propidium iodide/RNase staining based flow cytometric method relative to bortezomib | 30590258 | |
| RPMI8226 | Cell cycle assay | 1.7 uM | 48 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human RPMI8226 cells assessed as accumulation at S phase at 1.7 uM in presence of bortezomib after 48 hrs by propidium iodide/RNase staining based flow cytometric method relative to bortezomib | 30590258 | |
| RPMI8226 | Cell cycle assay | 1.7 uM | 48 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human RPMI8226 cells assessed as reduction in accumulation at G2/M phase at 1.7 uM in presence of bortezomib after 48 hrs by propidium iodide/RNase staining based flow cytometric method relative to bortezomib | 30590258 | |
| HaCaT | Antipyretic assay | 100 uM | 2 hrs | Antipyretic activity in human HaCaT cells assessed as inhibition of TNFalpha-induced PGE2 production at 100 uM pre-incubated for 2 hrs before TNFalpha stimulation for 24 hrs by ELISA | 31393125 | |
| OVCAR5 | Function assay | 300 uM to 1 mM | 72 hrs | Inhibition of NAPRT in human OVCAR5 cells assessed as potentiation of NAMPT inhibitor FK866-induced cytotoxicity by measuring reduction in cell viability at 300 uM to 1 mM incubated for 72 hrs by SRB assay | ChEMBL | |
| CCRF-CEM | Function assay | 3.5 mM | 48 hrs | Inhibition of NAPRT in human CCRF-CEM cells assessed as potentiation of NAMPT inhibitor FK866-induced apoptosis by measuring reduction in cell viability at 3.5 mM prer-incubated with IC50 level of FK866 for 48 hrs followed by compound addition and further | ChEMBL | |
| Jurkat | Function assay | 3.5 mM | 48 hrs | Inhibition of NAPRT in human Jurkat cells assessed as potentiation of NAMPT inhibitor FK866-induced apoptosis by measuring reduction in cell viability at 3.5 mM prer-incubated with IC50 level of FK866 for 48 hrs followed by compound addition and further i | ChEMBL | |
| ML2 | Function assay | 3.5 mM | 48 hrs | Inhibition of NAPRT in human ML2 cells assessed as potentiation of NAMPT inhibitor FK866-induced apoptosis by measuring reduction in cell viability at 3.5 mM prer-incubated with IC50 level of FK866 for 48 hrs followed by compound addition and further incu | ChEMBL | |
| NOMO | Function assay | 3.5 mM | 48 hrs | Inhibition of NAPRT in human NOMO cells assessed as potentiation of NAMPT inhibitor FK866-induced apoptosis by measuring reduction in cell viability at 3.5 mM prer-incubated with IC50 level of FK866 for 48 hrs followed by compound addition and further inc | ChEMBL | |
| NB4 | Function assay | 3.5 mM | 48 hrs | Inhibition of NAPRT in human NB4 cells assessed as potentiation of NAMPT inhibitor FK866-induced apoptosis by measuring reduction in cell viability at 3.5 mM prer-incubated with IC50 level of FK866 for 48 hrs followed by compound addition and further incu | ChEMBL | |
| NAMALWA | Function assay | 3.5 mM | 48 hrs | Inhibition of NAPRT in human NAMALWA cells assessed as potentiation of NAMPT inhibitor FK866-induced apoptosis by measuring reduction in cell viability at 3.5 mM prer-incubated with IC50 level of FK866 for 48 hrs followed by compound addition and further | ChEMBL | |
| Daudi | Function assay | 3.5 mM | 48 hrs | Inhibition of NAPRT in human Daudi cells assessed as potentiation of NAMPT inhibitor FK866-induced apoptosis by measuring reduction in cell viability at 3.5 mM prer-incubated with IC50 level of FK866 for 48 hrs followed by compound addition and further in | ChEMBL | |
| Raji | Function assay | 3.5 mM | 48 hrs | Inhibition of NAPRT in human Raji cells assessed as potentiation of NAMPT inhibitor FK866-induced apoptosis by measuring reduction in cell viability at 3.5 mM prer-incubated with IC50 level of FK866 for 48 hrs followed by compound addition and further inc | ChEMBL | |
| ARH77 | Function assay | 3.5 mM | 48 hrs | Inhibition of NAPRT in human ARH77 cells assessed as potentiation of NAMPT inhibitor FK866-induced apoptosis by measuring reduction in cell viability at 3.5 mM prer-incubated with IC50 level of FK866 for 48 hrs followed by compound addition and further in | ChEMBL | |
| RPMI8226 | Function assay | 3.5 mM | 48 hrs | Inhibition of NAPRT in human RPMI8226 cells assessed as potentiation of NAMPT inhibitor FK866-induced apoptosis by measuring reduction in cell viability at 3.5 mM prer-incubated with IC50 level of FK866 for 48 hrs followed by compound addition and further | ChEMBL | |
| U266 | Function assay | 3.5 mM | 48 hrs | Inhibition of NAPRT in human U266 cells assessed as potentiation of NAMPT inhibitor FK866-induced apoptosis by measuring reduction in cell viability at 3.5 mM prer-incubated with IC50 level of FK866 for 48 hrs followed by compound addition and further inc | ChEMBL | |
| NAMALWA | Function assay | 35 mg/kg | 45 days | Potentiation of NAMPT inhibitor 10 mg/kg, ip bid FK866-induced antitumor activity in human NAMALWA cells xenografted in SCID mouse assessed as increase in mouse survival at 35 mg/kg, ip bid up to 45 days | ChEMBL | |
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Biological Activity
| Description | Aspirin is a salicylate, and irreversible COX1 and COX2 inhibitor, used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains, as an antipyretic to reduce fever, and as an anti-inflammatory medication. Aspirin induces autophagy and stimulates mitophagy. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
| In vitro | ||||
| In vitro | Aspirin inhibits the activation of NF-kappa B, thus prevents the degradation of the NF-kappa B inhibitor, I kappa B, and therefore NF-kappa B is retained in the cytosol. Aspirin also inhibits NF-kappa B-dependent transcription from the Ig kappa enhancer and the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) long terminal repeat (LTR) in transfected T cells. [1] Aspirin and salicylate are mediated in part by their specific inhibition of IKK-beta, thereby preventing activation by NF-kappaB of genes involved in the pathogenesis of the inflammatory response. [2] Aspirin is protective against neurotoxicity elicited by the excitatory amino acid glutamate in rat primary neuronal cultures and hippocampal slices. [3] Aspirin triggers transcellular biosynthesis of a previously unrecognized class of eicosanoidsduring coincubations of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and neutrophils [polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN)]. Aspirin evokes a unique class of eicosanoids formed by acetylated PGHS-2 and 5-lipoxygenase interactions. [4] Aspirin treatment inhibits the phosphorylation of IRS-1 at Ser307 as well as the phosphorylation of JNK, c-Jun, and degradation of IkappaBalpha in 3T3-L1 and Hep G2 cells treated with tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha. Aspirin treatment inhibits phosphorylation of Akt and the mammalian target of rapamycin (but not extracellular regulated kinase or PKCzeta) in response to TNF-alpha. Aspirin rescues insulin-induced glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes pretreated with TNF-alpha. [5] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
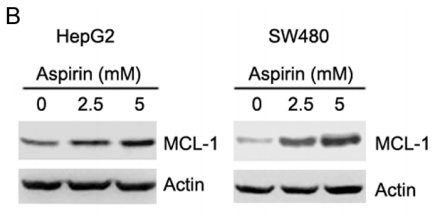
| Experimental Result Images | Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
| Western blot | MCL-1 p-AKT / AKT / p-ERK / ERK p-AMPKα / AMPKα / p-ACC / ACC SHH / SMO / GLI1 / Bcl-2 / Foxm1 |
|
26918349 | |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell proliferation Cell viability |
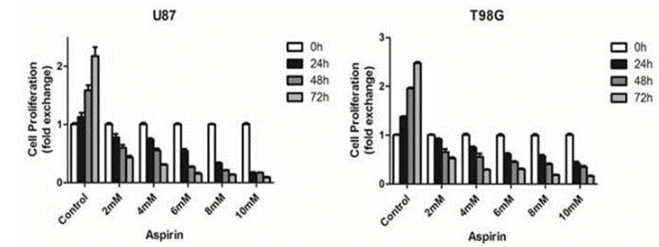
|
28446712 | |
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT06197009 | Not yet recruiting | Axial Spondyloarthritis | Sinocelltech Ltd. | July 1 2024 | Phase 2 |
| NCT05861128 | Not yet recruiting | Ankylosing Spondylitis | Suzhou Zelgen Biopharmaceuticals Co.Ltd | June 2024 | Phase 3 |
| NCT05868525 | Recruiting | Blunt Cerebrovascular Injury | Loma Linda University | April 2024 | Phase 4 |
| NCT05960864 | Not yet recruiting | Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) / Radiographic Axial SpA (r-axSpA)|Non-radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis (Nr-axSpA)|Axial Psoriatic Arthritis (axPsA)|Acute Anterior Uveitis (AAU)|Crohn Disease (CD)|Ulcerative Colitis (UC)|Reactive Arthritis (ReA) | Southwest Hospital China | February 2024 | -- |
| NCT06066983 | Recruiting | Autism Spectrum Disorder|Anxiety Disorders | Hugo W. Moser Research Institute at Kennedy Krieger Inc. | January 2024 | Not Applicable |
Chemical lnformation & Solubility
| Molecular Weight | 180.16 | Formula | C9H8O4 |
| CAS No. | 50-78-2 | SDF | Download Aspirin SDF |
| Smiles | CC(=O)OC1=CC=CC=C1C(=O)O | ||
| Storage (From the date of receipt) | |||
|
In vitro |
DMSO : 36 mg/mL ( (199.82 mM); Moisture-absorbing DMSO reduces solubility. Please use fresh DMSO.) Ethanol : 36 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molecular Weight Calculator |
|
In vivo Add solvents to the product individually and in order. |
In vivo Formulation Calculator |
||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Molarity Calculator
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Tech Support
Answers to questions you may have can be found in the inhibitor handling instructions. Topics include how to prepare stock solutions, how to store inhibitors, and issues that need special attention for cell-based assays and animal experiments.
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
* Indicates a Required Field
Tags: buy Aspirin | Aspirin supplier | purchase Aspirin | Aspirin cost | Aspirin manufacturer | order Aspirin | Aspirin distributor







































