
- Bioactive Compounds
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at [email protected] to customize your library.
You could select:
- Antibodies
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-DYKDDDDK Tag magnetic beads
- Anti-DYKDDDDK Tag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Poly DYKDDDDK Tag Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- New Products
- Contact Us
FCCP
Synonyms: Trifluoromethoxy carbonylcyanide phenylhydrazone, Carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone
FCCP (Trifluoromethoxy carbonylcyanide phenylhydrazone, Carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone) is a potent uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria that disrupts ATP synthesis by transporting protons across cell membranes.
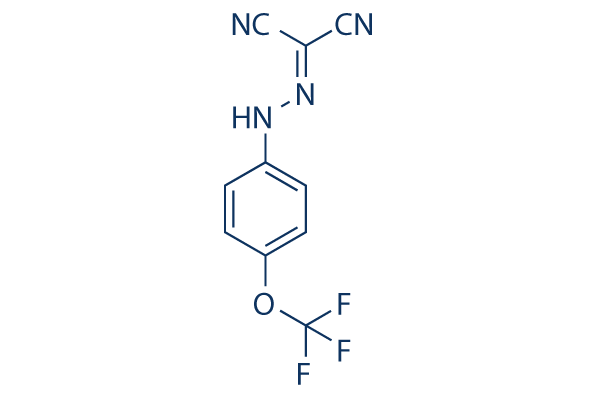
FCCP Chemical Structure
CAS: 370-86-5
Selleck's FCCP has been cited by 53 publications
Purity & Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.99%
99.99
Related compound libraries
Choose Selective OXPHOS Inhibitors
Cell Data
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T47D | Function assay | Inhibition of 1, 10-phenanthroline-induced HIF1 activation in human T47D cells by HRE3-TK-luciferase reporter gene assay, IC50=0.31μM | 20929261 | |||
| T47D | Function assay | Inhibition of hypoxia-induced HIF1 activation in human T47D cells by HRE3-TK-luciferase reporter gene assay, IC50=0.51μM | 20929261 | |||
| T47D | Function assay | 1 to 10 uM | Inhibition of HIF1-mediated induction of secreted VEGF level in 1, 10-phenanthroline-stimulated human T47D cells at 1 to 10 uM by ELISA | 20929261 | ||
| T47D | Function assay | 0.3 uM | 15 mins | Decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential in human T47D cells 0.3 uM after 15 mins by TMRM assay | 20929261 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Cytotoxicity assay | 1 uM | Cytotoxicity against human MDA-MB-231 cells assessed as inhibition of cell proliferation/viability at 1 uM | 23245650 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Cytotoxicity assay | 0.1 to 3 uM | Cytotoxicity against human MDA-MB-231 cells assessed as inhibition of cell proliferation/viability at 0.1 to 3 uM in presence of 0.1 uM rotenone mitochondrial electron transport inhibitor | 23245650 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Function assay | 0.3 uM | Stimulation of oligomycin-induced state 4 respiration in human MDA-MB-231 cells at 0.3 uM | 23245650 | ||
| T47D | Function assay | 0.1 to 3 uM | Effect on cellular respiration in human T47D cells assessed as increase in oxygen consumption at 0.1 to 3 uM | 22938093 | ||
| T47D | Function assay | 10 to 30 uM | Stimulation of state 4 cellular respiration in human T47D cells at 10 to 30 uM in presence of oligomycin | 22938093 | ||
| T47D | Function assay | 0.3 to 1 uM | Stimulation of state 4 cellular respiration in human T47D cells at 0.3 to 1 uM in presence of oligomycin | 22938093 | ||
| Hep3B | Function assay | 10 uM | Stimulation of state 4 cellular respiration in human Hep3B cells at 10 uM in presence of oligomycin | 22938093 | ||
| Hep3B | Function assay | 1 uM | Stimulation of state 4 cellular respiration in human Hep3B cells at 1 uM in presence of oligomycin | 22938093 | ||
| T47D | Function assay | 3 uM | 15 to 20 mins | Decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential in human T47D cells at 3 uM after 15 to 20 mins by TMRM assay | 22938093 | |
| TA3/Ha | Function assay | 6 uM | Induction of NAD(P)H oxidation in mouse TA3/Ha cells assessed as reduction of NAD(P)H/NAD(P)+ ratio at 6 uM by spectrofluorometer analysis | 24568614 | ||
| SH-SY5Y | Function assay | 10 uM | 5 mins | Inhibition of SOC in human SH-SY5Y cells assessed as reduction in thapsigargin-induced Ca2+ influx at 10 uM pre-incubated for 5 mins with 0.2 uM CsA followed by compound addition by FURA-2AM dye based fluorescence assay | 25265024 | |
| SH-SY5Y | Function assay | 10 uM | 10 mins | Induction of mitochondrial membrane potential loss in human SH-SY5Y cells at 10 uM incubated for 10 mins in presence of 0.2 uM CsA by TMRE dye based assay | 25265024 | |
| T47D | Function assay | 0.3 uM | 3 to 12 mins | Increase in oxygen consumption rate of mitochondrial state 4 respiration in human T47D cells assessed as reinitiation of oligomycin-stalled cellular respiration at 0.3 uM incubated for 3 to 12 mins by Clark-type oxygen electrode assay | 26637046 | |
| T47D | Function assay | 0.3 uM | 30 mins | Effect on mitochondrial membrane potential in human T47D cells at 0.3 uM after 30 mins by TMRM dye based fluorescence microscopy | 26637046 | |
| T47D | Function assay | 0.3 uM | Increase in oxygen consumption rate in digitonin permeabilized human T47D cells assessed as reinitiation of sodium azide-stalled cellular respiration at 0.3 uM by oxytherm Clark-type electrode assay in presence of ascorbate | 26637046 | ||
| HCT116 | Function assay | 2 uM | 30 mins | Induction of AMPK phosphorylation at Thr-172 residue in human HCT116 cells at 2 uM after 30 mins in glucose supplemented media by immunoblot method | 28233680 | |
| HCT116 | Function assay | 2 uM | 30 mins | Induction of AMPK phosphorylation at Thr-172 residue in human HCT116 cells at 2 uM after 30 mins in absence of glucose by immunoblot method | 28233680 | |
| DLD1 | Function assay | 1 uM | Induction of mitochondrial dysfunction in human DLD1 cells assessed as reduction in mitochondrial ATP production at 1 uM by Seahorse XF real-time assay | 31774672 | ||
| DLD1 | Function assay | 1 uM | Induction of mitochondrial dysfunction in human DLD1 cells assessed as increase in glycolytic ATP production at 1 uM by Seahorse XF real-time assay | 31774672 | ||
| LS174T | Function assay | 1 uM | Induction of mitochondrial dysfunction in human LS174T cells assessed as reduction in mitochondrial ATP production at 1 uM by Seahorse XF real-time assay | 31774672 | ||
| LS174T | Function assay | 1 uM | Induction of mitochondrial dysfunction in human LS174T cells assessed as increase in glycolytic ATP production at 1 uM by Seahorse XF real-time assay | 31774672 | ||
| DLD1 | Function assay | 1 uM | Uncoupling of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in human DLD1 cells at 1 uM in presence of oligomycin A by seahorse XFe96 analyser based assay | 31774672 | ||
| DLD1 | Function assay | 1 uM | Uncoupling of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in human DLD1 cells assessed as increase in oxygen consumption rate at 1 uM in presence of oligomycin A by seahorse XFe96 analyser based assay | 31774672 | ||
| HEK293 | Function assay | 1 to 3 uM | Inhibition of LiCl-activated Wnt signaling in HEK293 cells at 1 to 3 uM by TOPFlash reporter gene assay | 31774672 | ||
| KOPN8 | Function assay | 10 uM | 0.3 hrs | Induction of mitochondrial membrane potential loss in human KOPN8 cells at 10 uM after 0.3 hrs by TMRM staining based flow cytometric analysis | 31084028 | |
| HepG2 | Function assay | Luciferase/luciferin-expressing antifolate-resistant parasites were used to infect a culture of HepG2 cells that were pre-incubated with compounds. Infected hepatocytes emit light due to the luciferase reaction. Assay results are presented as the percent , IC50=0.245μM | ChEMBL | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Biological Activity
| Description | FCCP (Trifluoromethoxy carbonylcyanide phenylhydrazone, Carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone) is a potent uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria that disrupts ATP synthesis by transporting protons across cell membranes. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
| In vitro | ||||
| In vitro | FCCP treatment induces a very rapid 2-fold increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration that is accompanied by a strong protein synthesis rate inhibition. The translation inhibition correlates with an increased phosphorylation of the α subunit of eIF2 (eIF2α) and a 1.7-fold increase in the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase activity[1]. FCCP treatment also mildly decreases ATP and reactive oxygen species levels. It increases the expression of mitochondrial genes such as Tfam and COXIV while inducing morphological features of quiescent mouse HSCs and abrogating TGF-β signal transduction[2]. |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Research | Cell lines | PC12 cells | ||
| Concentrations | 30 μM | |||
| Incubation Time | 30 min, 1h, 2h | |||
| Method | Protein synthesis rate is assayed in 24-mm diameter multi-well dishes with fresh medium containing 0.175 Ci/mmol of [3H]methionine (200 μM), for 30 min at 37°C. PC12 cells are treated with FCCP for different period of times. |
|||
| In Vivo | ||
| In vivo |
FCCP significantly reduces mitochondrial membrane potential and ATP production in 8-cell mouse embryos and the number of inner cell mass cells within blastocysts with unchanged blastocyst development. This perturbed embryonic mitochondrial function is concomitant with reduced birth weight in female offspring following embryo transfer, which persists until weaning. Although FCCP-treated males also exhibits reduced glucose tolerance as female, but their insulin sensitivity and adiposity gain between 4 and 14 weeks is unchanged. Reducing mitochondrial function and, thus, decreasing ATP output in the precompacting embryo can influence offspring phenotype[3]. |
|
|---|---|---|
| Animal Research | Animal Models | Female C57BL/6 mice |
| Dosages | 1 mg/kg | |
| Administration | i.p. | |
Chemical lnformation & Solubility
| Molecular Weight | 254.17 | Formula | C10H5F3N4O |
| CAS No. | 370-86-5 | SDF | Download FCCP SDF |
| Smiles | C1=CC(=CC=C1NN=C(C#N)C#N)OC(F)(F)F | ||
| Storage (From the date of receipt) | |||
|
In vitro |
DMSO : 6 mg/mL ( (23.6 mM); Moisture-absorbing DMSO reduces solubility. Please use fresh DMSO.) Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molecular Weight Calculator |
|
In vivo Add solvents to the product individually and in order. |
In vivo Formulation Calculator |
||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Molarity Calculator
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Tech Support
Answers to questions you may have can be found in the inhibitor handling instructions. Topics include how to prepare stock solutions, how to store inhibitors, and issues that need special attention for cell-based assays and animal experiments.
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
* Indicates a Required Field
Tags: buy FCCP | FCCP supplier | purchase FCCP | FCCP cost | FCCP manufacturer | order FCCP | FCCP distributor







































