
- Bioactive Compounds
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at info@selleckchem.com to customize your library.
You could select:
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Antibodies
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-DYKDDDDK Tag magnetic beads
- Anti-DYKDDDDK Tag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Poly DYKDDDDK Tag Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- New Products
- Contact Us
Tolbutamide (HLS 831)
Tolbutamide (HLS 831) is an inhibitor of potassium channel, used for type II diabetes.
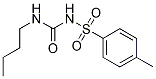
Tolbutamide (HLS 831) Chemical Structure
CAS: 64-77-7
Selleck's Tolbutamide (HLS 831) has been cited by 9 publications
Purity & Quality Control
Other Potassium Channel Products
Related compound libraries
Choose Selective Potassium Channel Inhibitors
Biological Activity
| Description | Tolbutamide (HLS 831) is an inhibitor of potassium channel, used for type II diabetes. | |
|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
| In vitro | ||||
| In vitro | Tolbutamide belongs to a class of medications called sulfonylureas. Tolbutamide lowers blood sugar by causing the pancreas to produce insulin (a natural substance that is needed to break down sugar in the body) and helping the body use insulin efficiently. This medication will only help lower blood sugar in people whose bodies produce insulin naturally. Tolbutamide is not used to treat type 1 diabetes (condition in which the body does not produce insulin and, therefore, cannot control the amount of sugar in the blood) or diabetic ketoacidosis (a serious condition that may occur if high blood sugar is not treated). Tolbutamide inhibits both the basal and the cyclic AMP-stimulated protein kinase activities and the IC50 of Tolbutamide is 4 mM. Similar Tolbutamide concentrations are required for half maximal inhibition of in vitro lipolysis induced by hormones (norepinephrine and ACTH) or by dibutyryl cyclic AMP plus theophylline. Tolbutamide also inhibits both soluble and membrane-bound protein kinase from canine heart. The Tolbutamide inhibition of adipose tissue cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase is one possible explanation for the antilipolytic effects of this drug. [1] Tolbutamide inhibits C6-glioma cell proliferation by increasing Cx43, which correlates with a reduction in pRb phosphorylation due to the up-regulation of the Cdk inhibitors p21 and p27. [2] Cytosolic nucelotides enhance the Tolbutamide sensitivity of the ATP-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic B cells by their combined actions at inhibitory and stimulatory receptors. [3] Tolbutamide inhibits glucagon-induced phosphorylation of the bifunctional enzyme protein in a dose-dependent manner. By adding 2 mM Tolbutamide, reduces activity of 6PF-2-K and increased activity of Fru-2,6-P2ase in the presence of 10(-9) M glucagon are partially restored. The present results suggest the possibility that Tolbutamide modulates the activity of hepatic 6PF-2-K/Fru-2,6-P2ase through inhibiting a phosphorylation of the enzyme protein. [4] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinase Assay | cAMP kinase assay | |||
| Diced epididymal fat pads from fed Wistar rats (175-225 gm) are obtained after decapitation and incubated at 37 °C for two hours in Krebs-bicarbonate buffer containing 1.27 mM CaCl2. When added, Tolbutamide is present only during the incubation. After incubation fat pads are rinsed and sonicated in cold Krebs-bicarbonate buffer. The aqueous supematants from centrifugation at 50,000 × g for 30 minutes at 4 °C contained 0.75 to 1.25 mg protein per mL and are assayed for cyclic AMP-stimulated protein kinase activity. The assay is performed in 0.2 mL with these additions, 10 μmoles sodium glycerofiosphate pH 7.0, 2 μmoles sodium fluoride, 0.4 μmoles theophylline, 0.1 μmoles ethylene glyool bis (β-aminoethyl ether)-N, N'-tetraaoetic acid, 3 μmoles magnesium chloride, 0.3 mg mixed histone, 2 nmoles (γ- 32P) ATP, 1 nmoles cyclic AMP when indicated, and 0.05 ml of supernatant. | ||||
| Cell Research | Cell lines | C6 glioma cells | ||
| Concentrations | 400 μM | |||
| Incubation Time | 24 hours | |||
| Method | C6 glioma cells are incubated in serum-free DMEM at 37 °C for at least 24 hours before each experiment. Tolbutamide (400 μM) is incubated for 24 hours in serum-free medium. Incubations are performed at 37 °C in an atmosphere of 95% air/5% CO2 with 90–95% humidity. | |||
| In Vivo | ||
| In vivo | 450 mg Tolbutamide/kg/day given for 7 days significantly increases the binding of insulin to isolated adipocytes. The binding curves reflect an increase in the number of receptor sites rather than in the affinity. The effect is associated with an enhanced response to insulin of the adipose tissue, since the fat cells obtained from animals treated with Tolbutamide convert significantly more glucose to lipids in the presence of insulin than those obtained from the control group. However, the augmentation of insulin binding sites is observed only at a large tolbutamide dosage, which reduces the pancreatic insulin content, the secretory response of the isolated pancreas, and the serum insulin levels. Smaller doses, sufficient to produce metabolic effects via a stimulation of insulin secretion, do not provide additional insulin binding sites. [5] | |
|---|---|---|
| Animal Research | Animal Models | Male albino Wistar rats (200-300 g) |
| Dosages | 450 mg/kg | |
| Administration | Tolbutamide is administered orally for 7 days. | |
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05830799 | Completed | Drug Interaction | Vicore Pharma AB | March 29 2023 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05097716 | Completed | Healthy Volunteers | Pfizer | November 2 2021 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03291288 | Completed | Drug Interaction Potential | Daiichi Sankyo Inc. | February 26 2018 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02819102 | Completed | Hereditary Angioedema | BioCryst Pharmaceuticals | March 2016 | Phase 1 |
Chemical lnformation & Solubility
| Molecular Weight | 270.35 | Formula | C12H18N2O3S |
| CAS No. | 64-77-7 | SDF | Download Tolbutamide (HLS 831) SDF |
| Smiles | CCCCNC(=O)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C | ||
| Storage (From the date of receipt) | |||
|
In vitro |
DMSO : 54 mg/mL ( (199.74 mM); Moisture-absorbing DMSO reduces solubility. Please use fresh DMSO.) Ethanol : 54 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molecular Weight Calculator |
Preparing Stock Solutions
Molarity Calculator
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Tech Support
Answers to questions you may have can be found in the inhibitor handling instructions. Topics include how to prepare stock solutions, how to store inhibitors, and issues that need special attention for cell-based assays and animal experiments.
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
* Indicates a Required Field
Tags: buy Tolbutamide (HLS 831) | Tolbutamide (HLS 831) supplier | purchase Tolbutamide (HLS 831) | Tolbutamide (HLS 831) cost | Tolbutamide (HLS 831) manufacturer | order Tolbutamide (HLS 831) | Tolbutamide (HLS 831) distributor








































