
- Bioactive Compounds
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at [email protected] to customize your library.
You could select:
- Antibodies
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-DYKDDDDK Tag magnetic beads
- Anti-DYKDDDDK Tag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Poly DYKDDDDK Tag Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- New Products
- Contact Us
Rifaximin
Rifaximin is a RNA synthesis inhibitor by binding the β subunit of the bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, used to treat traveler's diarrhea caused by certain bacteria.
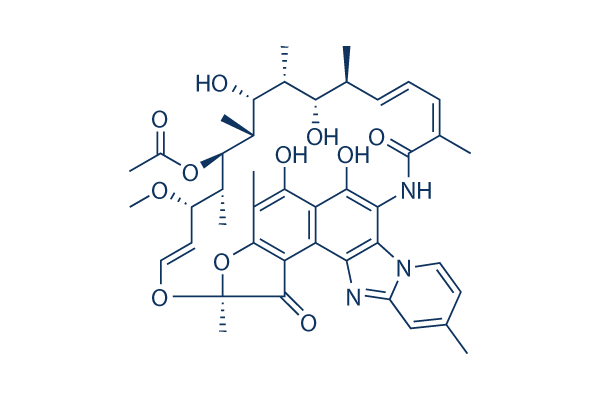
Rifaximin Chemical Structure
CAS: 80621-81-4
Selleck's Rifaximin has been cited by 1 publication
Purity & Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.98%
99.98
Other DNA/RNA Synthesis Products
Related compound libraries
Choose Selective DNA/RNA Synthesis Inhibitors
Biological Activity
| Description | Rifaximin is a RNA synthesis inhibitor by binding the β subunit of the bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, used to treat traveler's diarrhea caused by certain bacteria. | |
|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
| In vitro | ||||
| In vitro | Rifaximin (50 μM) reduces changes in the production of proinflammatory factors caused by LPS stimulation in IEC, such as TNF-α, IL-8, Rantes and PGE2 in normal intestinal epithelial cells. Rifaximin inhibits the LPS-induced cytokine and chemokine expression by suppressing NF-κB DNA-binding activity. Rifaximin (100 μM) effectively decreases the expression of TNFα, IL-8, MIP-3α and Rantes induced by LPS stimulation (100 μg/mL). [1] Rifaximin binds the β subunit of the bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, inhibiting the initiation of chain formation in RNA synthesis. Rifaximin has a lower MIC against gram-positive bacteria, with an MIC90 at dosages ranging from 0.01 µg/mL to 0.5 µg/mL. Rifaximin has broad-spectrum activity against aerobic and anaerobic gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. [2] |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | ||
| In vivo |
Rifaximin is highly concentrated in the intestinal tract compared with rifampicin. Rifaximin treatment results in significant induction of PXR target genes in the intestine of hPXR mice, but not in wild-type and Pxr-null mice. Rifaximin-mediated activation of human PXR, but not the other xenobiotic nuclear receptors constitutive androstane receptor, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)alpha, PPARgamma, and farnesoid X receptor. [3] Rifaximin could lead to PXR-dependent hepatocellular fatty degeneration as a result of activation of genes involved in lipid uptake, thus indicating a potential adverse effect of rifaximin on liver function after long-term exposure. [4] |
|
|---|---|---|
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05408910 | Not yet recruiting | Cystic Fibrosis|Abdominal Pain|Small Bowel Disease | Wake Forest University Health Sciences|Nationwide Children''s Hospital|University of Minnesota|University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center | January 2024 | Phase 2|Phase 3 |
| NCT04244877 | Withdrawn | Cirrhosis Liver|Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy|Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth|Gastrointestinal Motility Disorder | MetroHealth Medical Center | September 15 2021 | Phase 3 |
| NCT04841980 | Recruiting | Irritable Bowel Syndrome|Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth | University of Malaya | April 22 2021 | Phase 4 |
Chemical lnformation & Solubility
| Molecular Weight | 785.88 | Formula | C43H51N3O11 |
| CAS No. | 80621-81-4 | SDF | Download Rifaximin SDF |
| Smiles | CC1C=CC=C(C(=O)NC2=C(C3=C(C4=C(C(=C3O)C)OC(C4=O)(OC=CC(C(C(C(C(C(C1O)C)O)C)OC(=O)C)C)OC)C)C5=C2N6C=CC(=CC6=N5)C)O)C | ||
| Storage (From the date of receipt) | |||
|
In vitro |
Ethanol : 157 mg/mL DMSO : 47 mg/mL ( (59.8 mM); Moisture-absorbing DMSO reduces solubility. Please use fresh DMSO.) Water : Insoluble |
Molecular Weight Calculator |
|
In vivo Add solvents to the product individually and in order. |
In vivo Formulation Calculator |
||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Molarity Calculator
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Tech Support
Answers to questions you may have can be found in the inhibitor handling instructions. Topics include how to prepare stock solutions, how to store inhibitors, and issues that need special attention for cell-based assays and animal experiments.
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
* Indicates a Required Field
Tags: buy Rifaximin | Rifaximin ic50 | Rifaximin price | Rifaximin cost | Rifaximin solubility dmso | Rifaximin purchase | Rifaximin manufacturer | Rifaximin research buy | Rifaximin order | Rifaximin mouse | Rifaximin chemical structure | Rifaximin mw | Rifaximin molecular weight | Rifaximin datasheet | Rifaximin supplier | Rifaximin in vitro | Rifaximin cell line | Rifaximin concentration | Rifaximin nmr







































